MLflow.2.Automatic logging
인공지능,AI,학습,ML,Tensorflow, Cafee2,MLFlow/MLFlow# 참조 : https://dailyheumsi.tistory.com/258?category=980484
저번 Quick 리뷰 글에 이어 계속해서 작성한다.
이번 글은 MLflow 에서 제공하는 Automatic Logging 기능 예제들을 살펴본다.
사전 준비
다음이 사전에 준비 되어 있어야 한다.
# 파이썬 버전 확인
$ python --version
Python 3.8.7
# mlflow 설치 & 버전 확인
$ pip install mlflow
$ mlflow --version
mlflow, version 1.16.0
# 예제 파일을 위한 mlflow repo clone
$ git clone https://github.com/mlflow/mlflow.git
$ cd mlflow/examples
예제 살펴보기
linear_regression.py
examples 내에 있는 많은 예제 중, skelarn_autolog 를 사용해보자.
먼저 sklearn 을 설치해준다.
# sklearn 설치 & 버전 확인
$ pip install sklearn
$ python -c "import sklearn; print(sklearn.__version__)"
0.24.2skelarn_autolog/linear_regression.py 를 보면 다음처럼 생겼다.
# skelarn_autolog/linear_regression.py
from pprint import pprint
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
import mlflow
from utils import fetch_logged_data
def main():
# enable autologging
mlflow.sklearn.autolog()
# prepare training data
X = np.array([[1, 1], [1, 2], [2, 2], [2, 3]])
y = np.dot(X, np.array([1, 2])) + 3
# train a model
model = LinearRegression()
with mlflow.start_run() as run:
model.fit(X, y)
print("Logged data and model in run {}".format(run.info.run_id))
# show logged data
for key, data in fetch_logged_data(run.info.run_id).items():
print("\n---------- logged {} - ---------".format(key))
pprint(data)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()소스코드가 아주 간결하고 잘 설명되어 있다. 내용은 Linear Regression을 사용하는 간단한 머신러닝 코드다.
여기서는 2가지 코드가 눈에 띈다.
- mlflow.sklearn.autolog()
- Automatic Logging 기능을 사용하는 설정이다.
- 코드 앞부분에 들어가야 한다.
- with mlflow.start_run() as run:
- MLflow 의 실행(run) 의 시작을 알리는 컨텍스트 매니저 구문이다.
- run 에는 실행과 관련된 내용이 들어간다.
이제 다음 명령어로 실행해보자.
$ python sklearn_autolog/linear_regression.py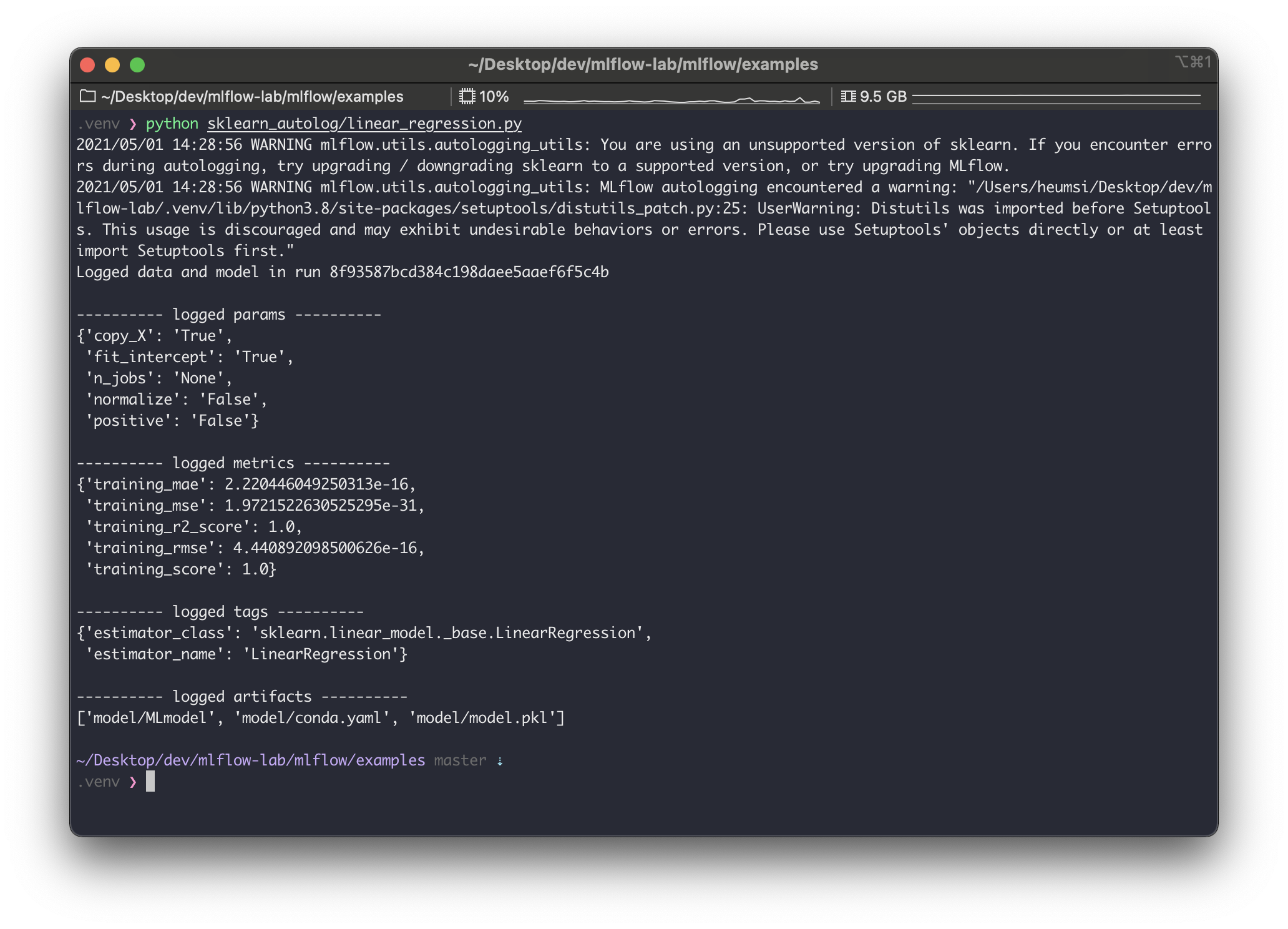
실행하고 나면 위와같은 출력이 나온다.
warning 은 일단 무시하면 될듯하고.. 로그를 좀 살펴보면, run_id 가 8f93587bcd384c198daee5aaef6f5c4b 로 생성되었고, 다음 사항들이 자동으로 기록한 것을 알 수 있다.
- params
- 모델 생성(위에서는 LinearRegression)에 사용하는 params 를 기록한다.
- 부연 설명하면... copy_X, fit_intercept 등의 파라미터는 LinearRegression 의 __init__ 파라미터다.
- metrics
- 모델 훈련 중에 평가하는 metrics를 기록한다.
- 위의 경우, mae, mse, r2_score, rmse, score (이건 뭔지 모르겠다.) 를 모두 기록해주었다.
- tags
- 이 실행에 관련된 tag 를 기록한다.
- 기본적으로 모델의 패키지와 클래스 이름을 기록한다.
- artifacts
- 실행에 대한 메타 정보와 모델 파일을 기록한다.
실제로 잘 생성되었는지 mlruns/ 에서 확인해보자.
$ tree mlruns/
8f93587bcd384c198daee5aaef6f5c4b 디렉토리에 각종 내용들이 로깅된 파일들이 있는 것을 볼 수 있다.
실제 어떤 값들이 들어가있는지 쉽게 보기위해 웹서버로 접속해서 봐보자.
$ mlflow ui
[2021-05-01 14:36:15 +0900] [87757] [INFO] Starting gunicorn 20.1.0
[2021-05-01 14:36:15 +0900] [87757] [INFO] Listening at: http://127.0.0.1:5000 (87757)
[2021-05-01 14:36:15 +0900] [87757] [INFO] Using worker: sync
[2021-05-01 14:36:15 +0900] [87759] [INFO] Booting worker with pid: 87759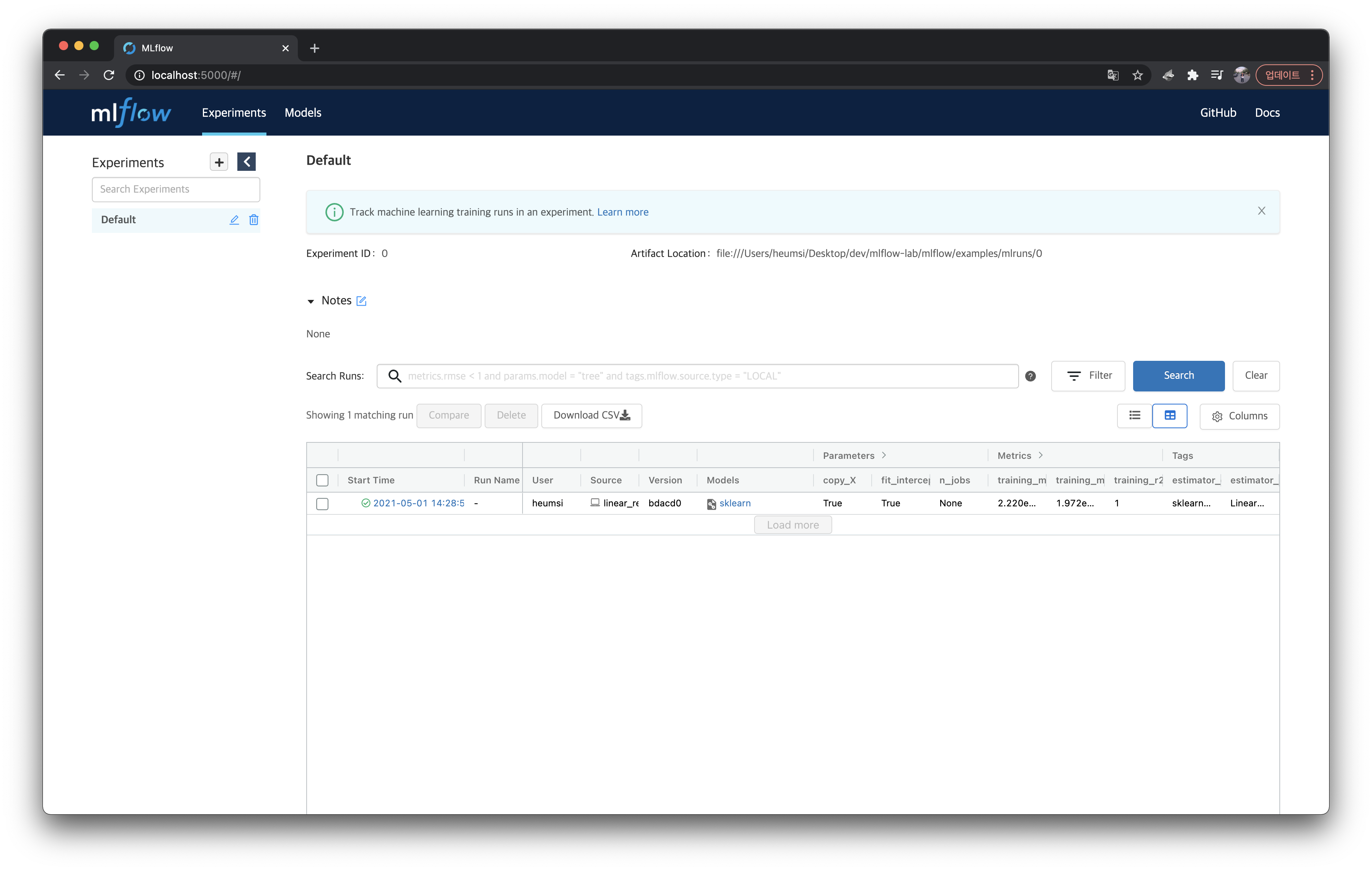
params , metrics, tags 등을 좀 더 자세히 확인해보기 위해 sklearn 모델을 클릭하여 실행 상세 페이지에 들어가보자.

위에서 출력한 내용들이 모두 잘 들어가있는 것을 볼 수 있다.
pipeline.py
이번엔 skelarn_autolog/pipeline.py 예제를 살펴보자.
이 파일은 다음처럼 생겼다.
from pprint import pprint
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
import mlflow
from utils import fetch_logged_data
def main():
# enable autologging
mlflow.sklearn.autolog()
# prepare training data
X = np.array([[1, 1], [1, 2], [2, 2], [2, 3]])
y = np.dot(X, np.array([1, 2])) + 3
# train a model
pipe = Pipeline([("scaler", StandardScaler()), ("lr", LinearRegression())])
with mlflow.start_run() as run:
pipe.fit(X, y)
print("Logged data and model in run: {}".format(run.info.run_id))
# show logged data
for key, data in fetch_logged_data(run.info.run_id).items():
print("\n---------- logged {} ----------".format(key))
pprint(data)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()sklearn.pipeline.Pipeline 을 사용하는 간단한 머신러닝 코드다.
바로 실행해보자.
$ python sklearn_autolog/pipeline.py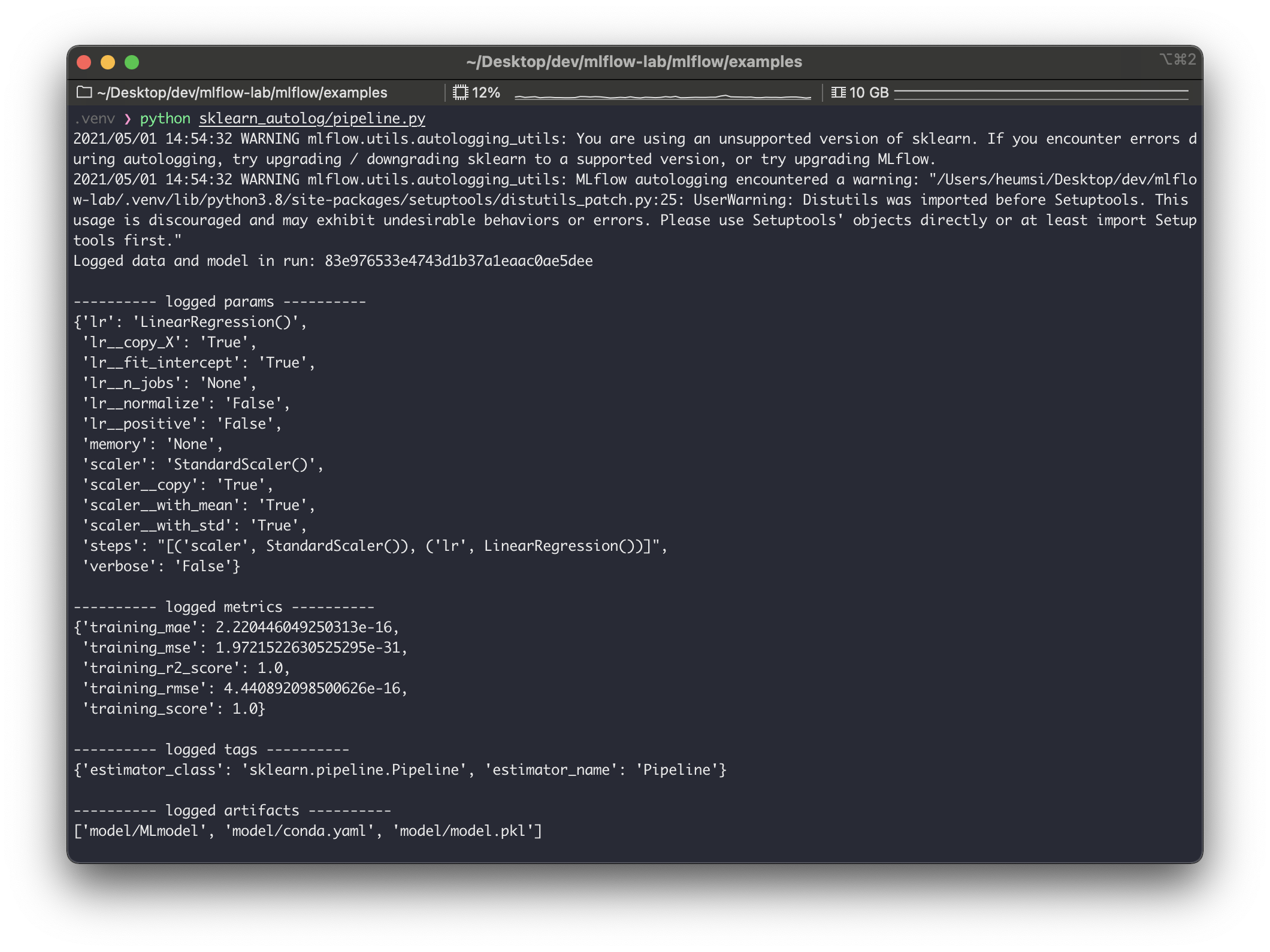
logged_params 를 보면 Pipeline 에 들어가는 모든 파라미터를 기록하는 것을 볼 수 있다.
기록된 값 역시 mlruns/ 에 저장된다.
grid_search_cv.py
마지막으로, skelarn_autolog/grid_search_cv.py 예제를 살펴보자.
다음처럼 생겼다.
from pprint import pprint
import pandas as pd
from sklearn import svm, datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
import mlflow
from utils import fetch_logged_data
def main():
mlflow.sklearn.autolog()
iris = datasets.load_iris()
parameters = {"kernel": ("linear", "rbf"), "C": [1, 10]}
svc = svm.SVC()
clf = GridSearchCV(svc, parameters)
with mlflow.start_run() as run:
clf.fit(iris.data, iris.target)
# show data logged in the parent run
print("========== parent run ==========")
for key, data in fetch_logged_data(run.info.run_id).items():
print("\n---------- logged {} ----------".format(key))
pprint(data)
# show data logged in the child runs
filter_child_runs = "tags.mlflow.parentRunId = '{}'".format(run.info.run_id)
runs = mlflow.search_runs(filter_string=filter_child_runs)
param_cols = ["params.{}".format(p) for p in parameters.keys()]
metric_cols = ["metrics.mean_test_score"]
print("\n========== child runs ==========\n")
pd.set_option("display.max_columns", None) # prevent truncating columns
print(runs[["run_id", *param_cols, *metric_cols]])
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()iris 데이터셋을 사용하고, svm 모델을 사용하는데, 이 때 GridSearchCV 를 사용하여 최적의 모델 파라미터를 찾는 머신러닝 코드다.
# show data logged in the parent run 아래 부분은 뭔가 양이 많은데, 그냥 로깅된 내용을 출력해주는 부분이므로, 여기서는 주의 깊게 봐지 않아도 된다.
아무튼 이 코드도 실행해보자.
$ python sklearn_autolog/grid_search_cv.py
출력된 내용을 보면 크게 parent run 과 child runs 으로 구성해볼 수 있다.
parent run 에서는 전체 파이프라인에 들어간 파라미터 값들을 기록하고, 또 이 GridSearch 를 통해 찾은 최적의 파라미터 값을 기록한다. (best_C, best_kernel ).
child runs 에서는 GridSearch 진행할 때 각각 파라미터 경우의 수대로 run 들을 실행하고 기록한 모습을 볼 수 있다. 이 때 child runs 들도 각각 하나의 run 이 되므로 run_id 를 가지게 된다. 즉 GridSearch 에서 파라미터 조합의 경우의 수가 많아지면, 그만큼의 실행(run) 이 생기게 된다.
실제 mlruns 를 확인해보면 이 child run 들이 생긴 것을 볼 수 있다.
(다만 parent run 과 별다른 디렉토리 구분은 없다. 즉 누가 child run 인지 디렉토리 구조로는 파악이 잘 안된다.)

그렇다면 웹서버에서는 어떻게 보여줄까?
웹서버에서도 child run 들을 parent run 들과 구분 없이 보여줄까?
이를 확인하기 위해 웹서버로 접속해서 확인해보자.

재밌게도 웹서버에서는 parent run 만 보인다.
grid_search_cv.py 가 있는 행에 + 버튼을 눌러보면 아래와 같이 child runs 가 나온다.

run 자체는 GridSearch 에 맞게 독립적으로 여러 개로 생성하되, run 간에 Parent, Child 관계를 가질 수 있는 것이다.
parent_run_id 로 mlruns 디렉토리를 검색해보면, 이러한 관계가 어떻게 구성될 수 있는지 알 수 있다.
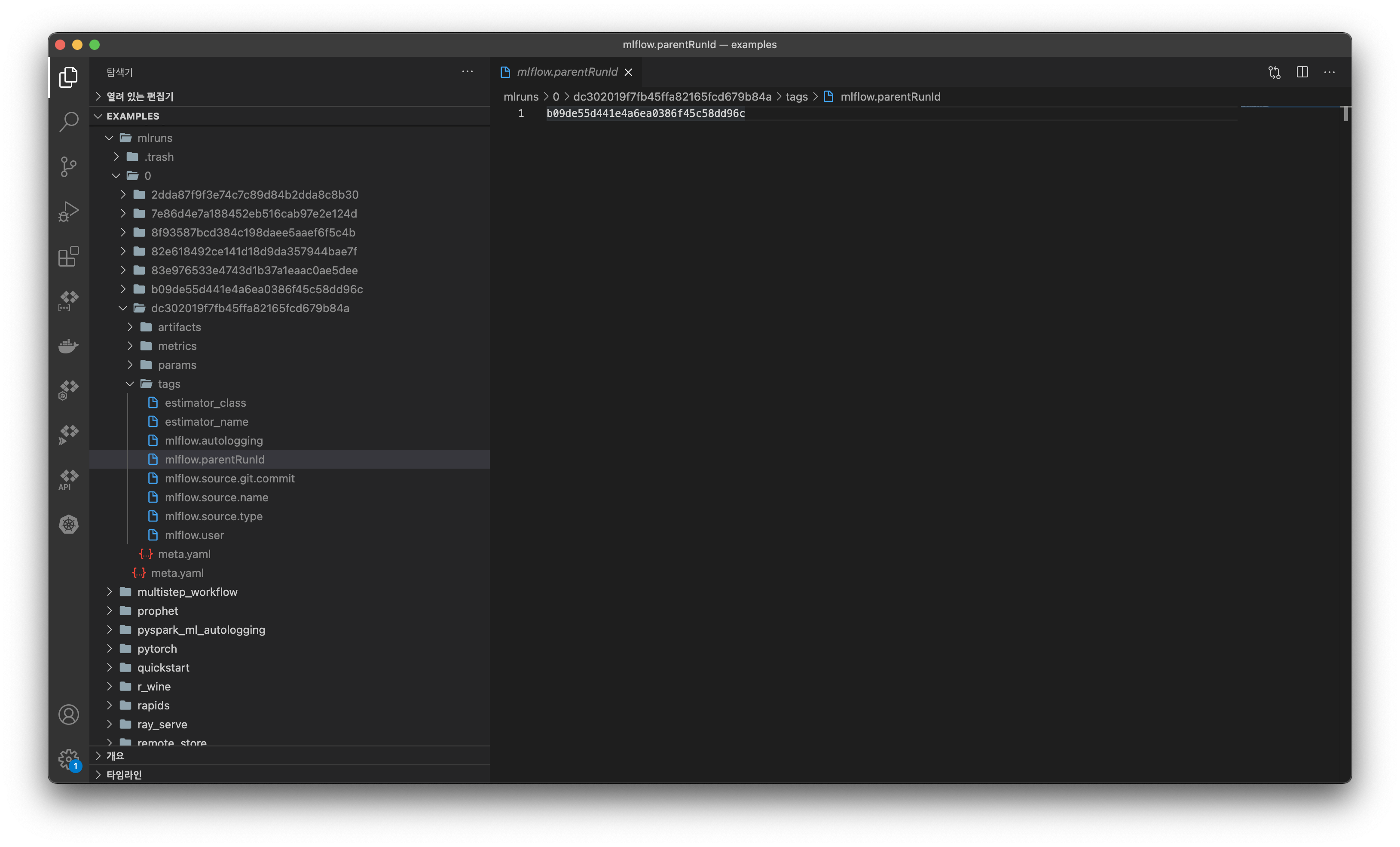
mlruns 에서 child run 의 디렉토리 구조를 살펴보면 tags/mlflow.parentRunId 가 있는 것을 볼 수 있다.
그리고 이 파일에 위 사진처럼 부모 run_id 가 기록되어 있다. (b09de55d441e4a6ea0386f45c58dd96c 는 dc302019f7fb45ffa82165fcd679b84a 의 parent run 이다.)
그리고 child run 은 artifact 과 관련하여 어떤 것도 기록하지 않고, metrics, params, tags 만 기록한다. artifacts 는 최종적으로 최적화된 모델을 사용하는 parent run 에서만 기록한다.
정리
- mlflow.sklearn.autolog() 기능으로 로깅 함수를 쓰지 않아도 자동 로깅을 사용할 수 있다.
- autolog() 는 머신러닝 프레임워크별로 지원한다. 이에 대한 내용은 여기에서 확인하자.
- artifacts ,params, metrics, tags 등을 모두 기록한다.
- GridSearch 를 쓰는 경우 여러 개의 run 들을 만들어 실행하고 기록한다.
- run 은 parent run 과 child run 으로 구성된다.
- child run 은 GridSearch 에 사용되는 파라미터 별로 실행한다.
- parent run 은 child run 중 가장 최적화된 파라미터를 가지고 실행한다.
- parent run 만 artifacts 를 기록한다.
- 웹서버에서도 parent - child 구조를 확인할 수 있다.
이전 글에서 모델러가 로깅을 위해 mlflow 를 알고 써야하는 의존성에 대해서 걱정했었는데, 자동 로깅 기능을 사용하면 이러한 걱정이 좀 많이 내려가지 않을까 싶다.
'인공지능,AI,학습,ML,Tensorflow, Cafee2,MLFlow > MLFlow' 카테고리의 다른 글
| MLflow.5.Model Registry (0) | 2021.12.27 |
|---|---|
| MLflow.4.Tracking Server (0) | 2021.12.27 |
| MLflow.3.Experiments & Runs (0) | 2021.12.24 |
| MLflow.1.Quick Review ( 오작동 일부 수정 ) (0) | 2021.12.17 |
| MLFlow.DB.확인방법 (0) | 2021.08.31 |